
MailScan
3.1a for SMTP Servers provides Virus Security, Content Security and Spam
Security for any organization's e-mail server. It is positioned in the path of
SMTP traffic and all the e-mails pass through MailScan before reaching the
destination.
| When
an e-mail is received: |
||||||||||
It
is dis-assembled into the following components:
|
||||||||||
| Its'
body and the attachments pass through the Virus-Analyzer and the
Content-Analyzer. |
||||||||||
Depending
on the results given by the Virus-Analyzer and the Content-Analyzer, the
mail is either:
|
||||||||||
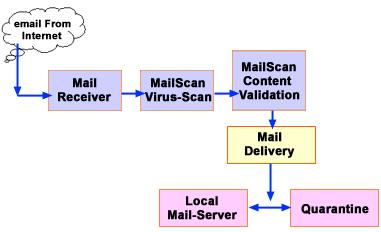
| Mail
Receiver: MailScan has a comprehensive SMTP receiver daemon. Termed as the SMTPD-SMTP Server, the daemon receives the mail from the sender and saves the it in the spool directory for further processing. The SMTP receiver daemon is a multi-threaded module that can handle heavy e-mail traffic loads. MailScan's SMTP Server can prevent unauthorized relaying by using two techniques:
|
||||||
| Message
Dis-assembly The MailScan Dispatcher splits each e-mail message into various components such as the header, the body and the attachments. Compressed formats (ZIP, ARJ, etc.) are scanned for viruses and cleaned. |
| MailScan
Content Validation: |
||||||||
Each
and every attachment (including the body, if it is in HTML format) is
checked for:
|
||||||||
| Mail
Delivery |
||||||||
Depending
on the results of content and attachment validation, the e-mail is
either:
|
||||||||
| As
and when required, warning messages to the sender, the recipient and the
administrators can be generated. |
||||
|
||||
[LOOKING FOR DRIVERS - CLICK HERE]
You are visitor number: